Ayurveda

"Revitalize Your Performance: Sports Massage for Peak Athletic Potential"
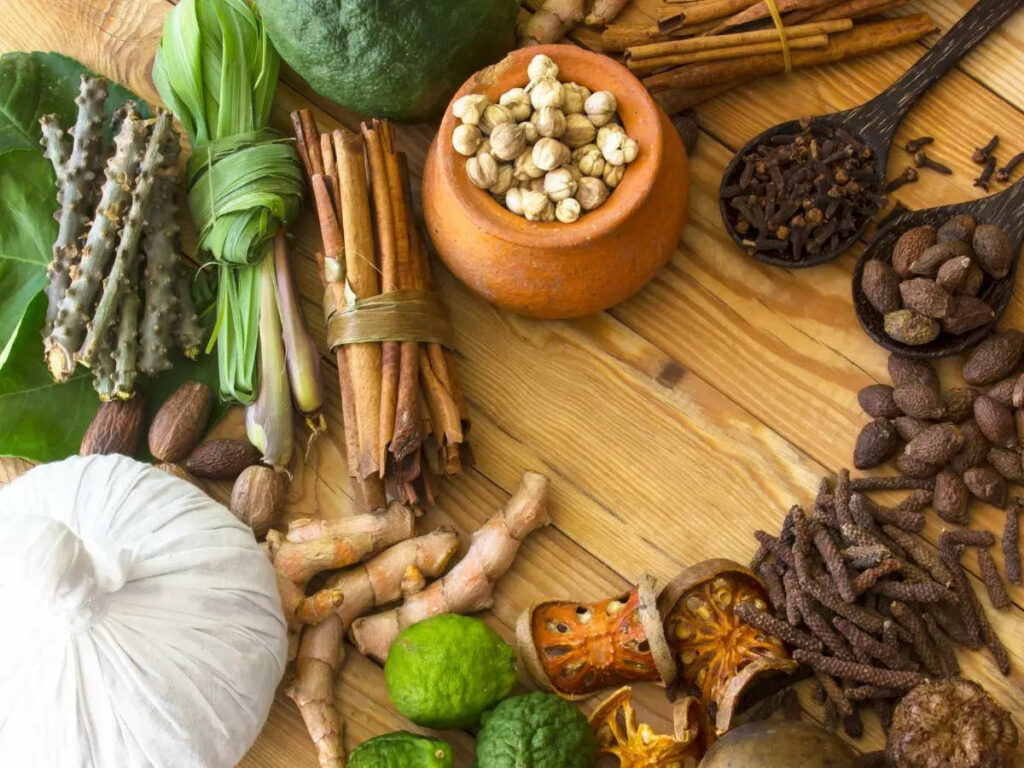
Ayurveda, also called Ayurvedic medicine, traditional system of Indian medicine. Ayurvedic medicine is an example of a well-organized system of traditional health care, both preventive and curative, that is widely practiced in parts of Asia. Ayurveda has a long tradition behind it, having originated in India perhaps as much as 3,000 years ago. Today it remains a favored form of health care in large parts of the Eastern world, especially in India, where a large percentage of the population uses this system exclusively or combined with modern medicine.
Ayurveda - The Science of Life

Ayurveda is derived from two Sanskrit root words: Ayu, which means Life, and Veda, which means Knowledge. Thus we can also call Ayurveda the ‘Science of life’ more than a mere system of treating an illness. Ayurveda is also known as the science of natural healing because it derives its medicines purely from nature. Ayurveda originated in India and is 5000 years old medical knowledge system. According to Ayurveda, body, mind, and spirit are connected. Most of Ayurveda is connected with the cures accessible from nature. It also deals with the root cause of the problem and is a permanent cure in most cases. In most cases, a patient treated with Ayurveda not only gets cured but also gets permanent immunity. The main advantage that Ayurveda has over homeopathy is that the former just uses natural means to cure a disease and is the most eco-accommodating approach to getting cured. It has been proved that –
“Ayurveda is the mother of all the medication”


History of Ayurveda

Ayurveda is attributed to Dhanvantari, the physician to the gods in Hindu mythology, who received it from Brahma. Its earliest concepts were set out in the portion of the Vedas known as the Atharvaveda (c. 2nd millennium BCE). The period of Vedic medicine lasted until about 800 BCE. The Vedas are rich in magical practices for the treatment of diseases and in charms for the expulsion of the demons traditionally supposed to cause diseases. The chief conditions mentioned are fever , cough, consumption, diarrhea, dropsy (generalized edema), abscesses, seizures, tumors, and skin diseases (including leprosy). The herbs recommended for treatment are numerous.
The golden age of Indian medicine, from 800 BCE until about 1000 CE, was marked especially by the production of the medical treatises known as the Caraka-samhita and Susruta-Samhita, attributed respectively to Caraka, a physician, and Susruta, a surgeon. Estimates place the Caraka-samhita in its present form as dating from the 1st century CE, although there were earlier versions. The Susruta-Samhita probably originated in the last centuries BCE and had become fixed in its present form by the 7th century CE. Of somewhat lesser importance are the treatises attributed to Vagbhata. All later writings on Indian medicine were based on these works, which analyze the human body in terms of earth, water, fire, air, and ether as well as the three bodily humors (Vata, pitta, and Kapha).
Ayurveda is attributed to Dhanvantari, the physician to the gods in Hindu mythology, who received it from Brahma. Its earliest concepts were set out in the portion of the Vedas known as the Atharvaveda (c. 2nd millennium BCE). The period of Vedic medicine lasted until about 800 BCE. The Vedas are rich in magical practices for the treatment of diseases and in charms for the expulsion of the demons traditionally supposed to cause diseases. The chief conditions mentioned are fever , cough, consumption, diarrhea, dropsy (generalized edema), abscesses, seizures, tumors, and skin diseases (including leprosy). The herbs recommended for treatment are numerous. The golden age of Indian medicine, from 800 BCE until about 1000 CE, was marked especially by the production of the medical treatises known as the Caraka-samhita and Susruta-Samhita, attributed respectively to Caraka, a physician, and Susruta, a surgeon.
“Ayurveda is the mother of all the medication”
Estimates place the Caraka-samhita in its present form as dating from the 1st century CE, although there were earlier versions. The Susruta-Samhita probably originated in the last centuries BCE and had become fixed in its present form by the 7th century CE. Of somewhat lesser importance are the treatises attributed to Vagbhata. All later writings on Indian medicine were based on these works, which analyze the human body in terms of earth, water, fire, air, and ether as well as the three bodily humors (Vata, pitta, and Kapha).
Ayurvedic Body Types
Ayurveda is based on the principles of three Dosha or the three basic energy types which are further classified as Vata, pitta & kapha. According to Ayurveda, these Dosha or energies can be found in everyone and everything thus making them the essential building blocks of the material world. All three Dosha combine to create different climates, different foods, different species, and even different individuals within the same species and perform different physiological functions in every individual body. The particular ratio of Vata, pitta, and kapha within each of us has a significant influence on our individual physical, mental, and emotional character traits. Here’s explaining to you the three Dosha and the different functions they perform within the body.
Kapha, one of the three doshas in Ayurveda, is primarily composed of the earth and water elements. It is the fundamental energy that imparts solidity and structure to all things, ensuring the maintenance of their specific forms. Kapha plays a crucial role in controlling growth within the body and distributing water to all its parts. This dosha is responsible for keeping the body's cells well-hydrated, facilitating joint lubrication, moisturizing the skin, sustaining immunity, and safeguarding the body's tissues. In a state of balance, Kapha manifests as love and forgiveness, contributing to emotional well-being. However, when Kapha becomes imbalanced, it can result in feelings of insecurity and envy, affecting both physical and emotional health. Understanding and managing one's Kapha dosha is a key aspect of Ayurvedic health and wellness practices.
Vata, one of the fundamental doshas in Ayurveda, is primarily constituted of the space and air elements. It embodies the energy associated with creativity, adaptability, and movement. Vata is responsible for regulating a wide range of bodily functions connected to motion, encompassing blood circulation, respiration, blinking, tissue mobility, cellular motility, heartbeat, and the intricate communication between the mind and the nervous system. When an imbalance of Vata Dosha arises within the body, it can manifest as emotional and physical disturbances, often giving rise to feelings of fear and anxiety. Ayurveda emphasizes the significance of understanding and managing Vata to maintain overall well-being. This involves the adoption of specific lifestyle practices, dietary choices, and therapies.
Pitta, one of Ayurveda's three doshas, is primarily composed of fire and water elements, characterized by qualities such as hot, sharp, light, liquid, oily, and subtle. Unlike other doshas, Pitta is neither mobile nor stable; it tends to disperse throughout the body. Pitta is responsible for regulating the body's metabolic systems, encompassing vital functions like digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation. In a state of balance, Pitta bestows attributes of contentment and intelligence. However, an imbalance in Pitta Dosha can lead to various issues, including the development of ulcers and heightened feelings of anger. Understanding and managing Pitta Dosha are central to Ayurvedic principles, involving specific dietary choices, lifestyle adjustments, and therapeutic interventions aimed at maintaining Pitta's equilibrium.
Panchamahabhutas
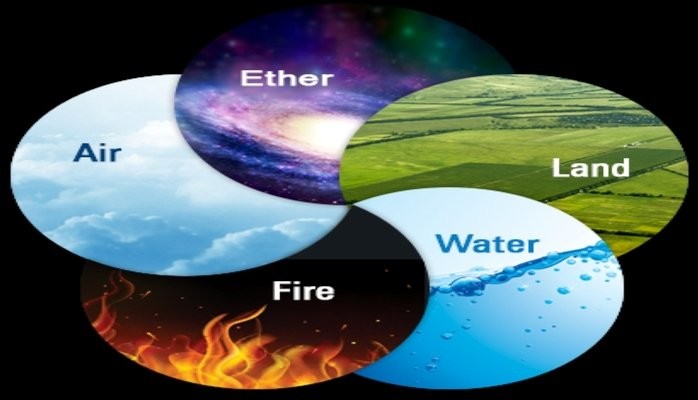
Ayurveda believes that everything in this universe is made up of five basic elements. These elements are classified as earth (Prithvi), water (jal), fire (Agni), wind (Vayu) & space, or ether (Akash). Collectively these five basic elements are known as Panchamahabhutas.
Since, Ayurveda believes that the components and functioning of nature are similar to the functioning of the human body, the concept of Panchamahabhutas is considered to be the foundation of Ayurveda and also pivotal to the understanding of the functioning and movement of the human body.
These Panchmahabutas are present in every being (living or non-living), substance, material, and object that are present in the universe. These elements can also be called mahabhutas due to their large size in comparison to their precursor bhutas (minute forms of mahabhutas) or due to their extensive presence. But in a nutshell, the fact remains that everything in the creation is made up of these Panchamahabhutas and there is nothing present in this universe that can be called devoid of these 5 elements.
“Ayurveda is the mother of all the medication”

Reason Why Ayurveda Is Best Medicinal System
-
Ayurveda does not have any side effect
-
Ayurveda Cures The Root Problem and Not Just Symptoms
-
Ayurveda treats body as a whole
-
Ayurvedic medicine are cost-effective
-
Ayurveda is a lifestyle
-
Ayurveda involves more than the herbs
-
Ayurveda for mild and chronic diseases
-
Ayurveda emphasizes both prevention as well as cure
-
yurveda helps you understand yourself
Ayurveda treatments and medicines are free from any side effects. Adverse side-effects occur in the western system of medicine due to chemical overdose or mismatch in your body. Ayurveda medicines are all chemical-free and based on primitive herbs and natural supplements from nature.

Ayurveda is not a healing system that provides instant relief from symptoms. Holistic medicine aims to restore health by understanding the underlying causes of diseases. It strives to attack the root causes and detoxify, cleanse, strengthen body tissues (dhatus), and balance bodily doshas, ensuring a complete cure.

Ayurvedic is not only one of the world’s oldest systems of medicine but also holistic (whole-body) in nature. Ayurveda embraces the whole of you and acknowledges the connection between your mind, body, and soul. Traditional medicine believes that creating this harmony can prevent illness, treat acute conditions, and contribute to a hale and hearty life.
Ayurveda Traditional MedicineAyurveda, the traditional Indian medicine, may be the most ancient but it is also the most effective, safest, cost-effective treatment of all. Ayurveda medicines are reasonable compared to expensive Western drugs. Some of the Ayurvedic medicines can be even made at home from herbs and ingredients in your kitchen making it easy and convenient.
Ayurveda places great importance on one’s path, or lifestyle which involves one’s diet, physical exercise, mental well-being, and other daily routines or dinacharyas to improve the overall quality of life. According to this powerful science of permanent healing, following an Ayurvedic dinacharya is one of the best things that you can do to maintain body balance, prevent diseases, treat all ailments, and stay in complete control.
Ayurveda treatment snot involves herbs and numerous other substances like milk, honey, oils, ghee, butter, minerals, to ashes. Herbs are mainly used in Ayurveda therapies and also in Ayurveda medicines. Reaming numerous substances is used equally depending upon the disease and individual body condition.
Most of the time, the science of Ayurveda is based on the various compounds that make run your body. Ayurveda tries to treat underlying causes of problems rather than a part of the body's organ that is affected. Ayurveda treatment effectively treats chronic diseases and the mind and brings back to body equilibrium.

Ayurveda believes that “Prevention is better than cure” and gives immense importance to the same. It teaches a range of daily routines for complete control and balance of Dosha and ensures optimum health. Ayurveda also lays down numerous methods, medicines, and measures to permanently cure diseases and prevent future reoccurrence.

Ayurveda is not just a diet or an exercise program. On the contrary, it is a time-tested body of immense wisdom that helps you understand and love yourself. Ayurveda considers this vital to your health and happiness and an Ayurveda physician can help you understand your bodily Dosha, physical, mental, and emotional qualities, and what works for you.
Ayurveda Is Recognized By The WHO
Ayurveda is recognized by the WHO system of medicine. WHO has included Ayurveda in its Traditional Medicine Strategy, which encourages member states to develop policies and regulations related to traditional medicines, including Ayurveda. WHO has also developed criteria for the quality assurance and safety of traditional medicines, including Ayurveda. WHO has also established a Traditional Medicine Strategy Implementation Network (TMSIN), which is a global network of experts in traditional medicine. This network guides the development and implementation of traditional medicine policies and regulations, including those related to Ayurveda. In addition, WHO has included Ayurveda in its care. This list includes herbal, mineral, and biological medicines, including those used in Ayurveda. WHO has also included Ayurveda in its Model List of Essential Medicines, making it available to primary healthcare providers around the world.
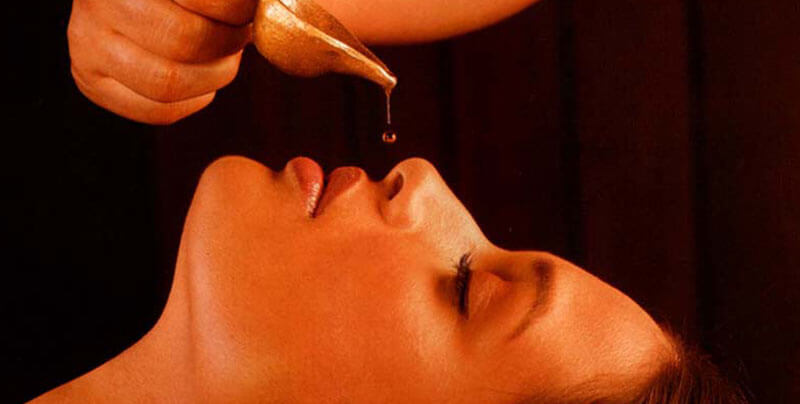

Nasya Therapy

The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes Ayurveda as a valid Nasya therapy is an Ayurvedic practice that involves the administration of herbal oils through the nose. It is believed to help clear blockages from the head and sinuses, reduce stress, strengthen the immune system, and improve vision. Modern health and science practices have shown that Nasya therapy can be beneficial for a variety of conditions. It has been shown to help improve respiratory health, reduce nasal congestion and blockages, improve sinus health, and alleviate headaches, colds, and allergies. It can also help reduce stress and improve sleep quality. Nasya therapy works by introducing oil or herbal extracts into the nasal passages. The oil or extract is believed to penetrate the mucous membranes, providing a cleansing, healing, and cooling sensation. The oils used in Nasya therapy are thought to help lubricate, cleanse, and soothe the nasal passages. The herbs used in the therapy can also help to reduce inflammation and provide a calming effect. Nasya therapy is usually administered by an experienced practitioner. The practitioner will use a special instrument to deliver the oil or herbs into the nostrils. The amount of oil or herbs used will depend on the patient’s individual needs. After the oil or herbs are delivered, the practitioner will then massage the area around the nose and forehead to help stimulate circulation and increase absorption.
“Ayurveda is the mother of all the medication”
Shodhana Therapy
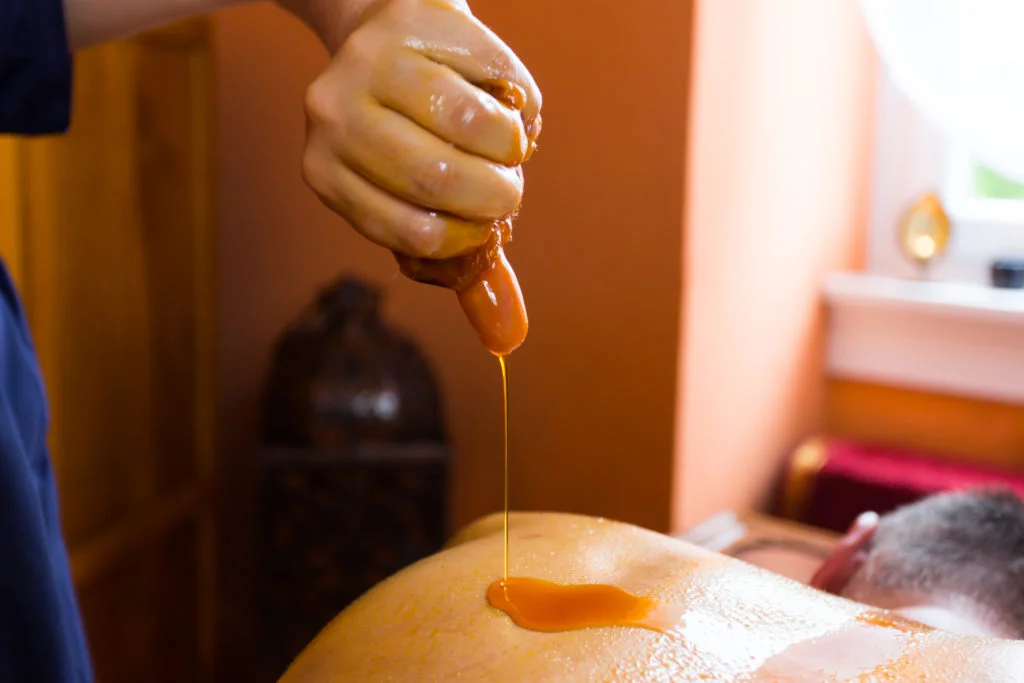

It is an Ayurvedic healing practice that focuses on the purification of the body and mind. It works by using methods such as oil massage, steam therapy, sweat therapy, enema, fasting, and purgation. These treatments help to remove toxins from the body and restore balance. Modern health and science practices have shown that Shodhana therapy can help improve overall health and well-being by flushing out accumulated toxins in the body, stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms, and helping the body to better absorb nutrients. One key benefit of Shodhana therapy is its ability to help the body detoxify and rid itself of dangerous toxins like heavy metals, pesticides, and environmental pollutants. By flushing out these toxins, the body can better absorb essential nutrients and promote a healthy balance of hormones. such practice is not only conducted for the body but for food processing as well. According to “Traditional and ayurvedic foods of Indian Origin”, “Shoshana therapy is a type of purification treatment where toxic factors are eliminated from foods by the application of various unit operations.”Another benefit of Shodhana therapy is its ability to boost immunity. By encouraging the body’s natural detoxification process, Shodhana therapy can help the body fight off infections and diseases. In addition, Shodhana therapy can help to improve digestion, reduce inflammation, and improve sleep quality.


Diabetes & Ayurveda

Diabetes is a serious threat to a person of any age. This is attributed to poor lifestyle, bad diet, and lack of exercise. Ayurveda recommends fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet, a healthy lifestyle, and quitting caffeine. Apart from this, the consumption of herbs such as turmeric can greatly help to keep blood sugar at the optimum level. Practicing breathing techniques and yoga can further help to keep diabetes under control.



